Bush Stone-curlew
Bush Stone-curlewBurhinus grallarius | |
|---|---|
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Aves |
| Order: | Charadriiformes |
| Family: | Burhinidae |
| Status | |
| World: | Least concern (IUCN) |
| Australia: | Not listed in EPBC Act 1999 |
| Victoria: | Critically Endangered (FFG Threatened List 2023) |
| NSW: | Endangered (TSCA 1995)* |
| South Australia: | Rare (NPWA 1972)* |
| VIC FFG: | Action Statement No. 78 (pdf) |

The Bush Stone-curlew (Burhinus grallarius) is a large, ground-dwelling bird of extraordinary grace and beauty. It is endemic to Australia and nearby islands. It was formerly known as the Bush Thick-knee.
Although the Bush Stone-curlew looks rather like a wader and is related to the oystercatchers, avocets and plovers, it is a dry-land predator: essentially a winged terrestrial carnivore.
Distribution
Bush Stone-curlews remain reasonably common in the north of Australia, but have become rare in the more fertile southern parts of Australia, particularly in Victoria where they are Critically Endangered.
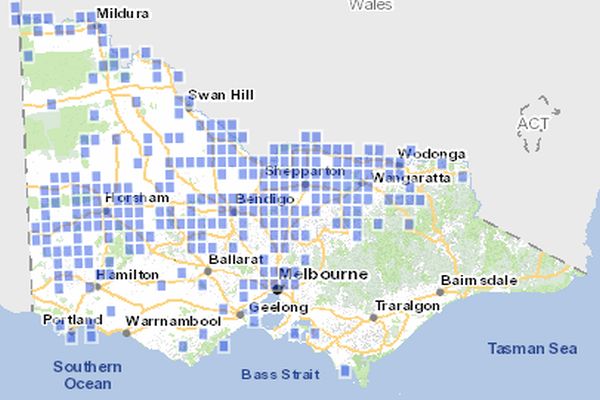
By 1970 there had been a significant reduction in the geographic distribution of Bush Stone-curlews in many areas of Victoria, particularly in the west, south and central Victoria where the species has been lost.
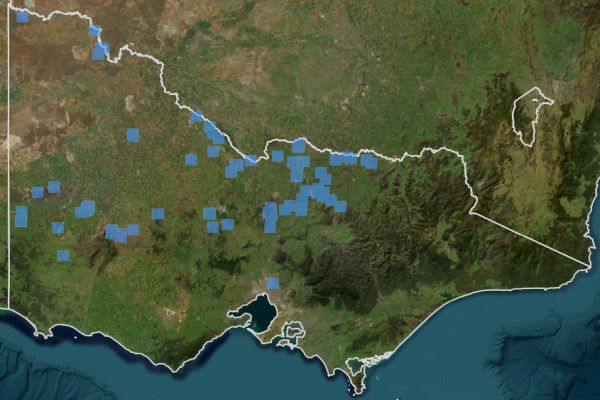
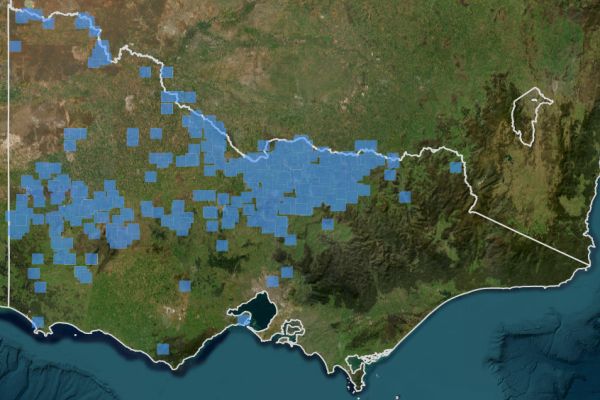
Bush Stone-curlew 2000 to 2024.
By 2000 there had been a considerable and dramatic loss of the Bush Stone-curlew across much of Victoria placing this species on the FFG Threatened List as Critically endangered..
Map source: VVB 2025.
Ecology & Habitat

During the day, Bush Stone-curlews tend to remain inactive, sheltering amongst tall grass or low shrubs and relying on their cryptic plumage to protect them from their only natural predators: raptors.
When disturbed, they freeze motionless, often in odd-looking postures. For visual predators like raptors (and humans), this works well, but it serves little purpose with introduced feral animals that hunt by scent: notably foxes.
Despite their ungainly appearance and habit of freezing motionless, they are sure-footed, fast and agile on the ground, and although they seldom fly during daylight hours, they are far from clumsy in the air; flight is rapid and direct on long, broad wings.
Feeding
Like most stone-curlews, it is mainly nocturnal and specialises in hunting small grassland animals: frogs, spiders, insects, molluscs, crustaceans, snakes, lizards and small mammals are all taken, mostly gleaned or probed from soft soil or rotting wood; also a few seeds or tubers, particularly in drought years. Birds usually forage individually or in pairs over a large home range, particularly on moonlit nights.
Breeding
Curlews nest on the ground, the first eggs to hatch will often be in early spring and chicks are unable to fly for first two months. The mother doesn’t feed the chicks, but just points the chicks to food. The chick must learn to eat or die but this is dependent on there being suitable habitat which supports insects, beetles’ lizards, frogs etc., all in close proximity to their nest.
Threats
Most experts believe that fox predation is a prime factor in the decline of Bush Stone -curlews, however there are areas where foxes are common yet the Bush Stone-curlew population remains healthy, so considerable uncertainty remains. Large-scale habitat destruction and fragmentation has undoubtedly been important.
Maintaining a complex ground cover of leaves, twigs and logs which support insects and other food for the Bush Stone-curlew is critical.
Burning is a major threat, particularly in isolated remnant habitats as it can remove all ground cover creating a barren zone thus starving birds or forcing them into open landscapes where they cannot survive.
Conservation & Management
Planning
Facilitate the protection of known Bush Stone-Curlew populations through local and bioregional planning and develop or amend planning scheme overlays and schedules.
Predator control
Encourage landholders in Bush Stone-curlew areas to initiate effective fox control measures.
Habitat retention/enhancement
Encourage landholders to fence off woodland remnants that are in unimproved pasture and have an intact layer of native ground-cover plants.
Encourage landholders to leave fallen branches and debris on the ground beneath trees at key known or potential curlew habitat sites.
Education
Provide landholder and community extension services relating to the Bush Stone-curlew, particularly Golf Courses and Land for Wildlife properties. Provide advice on increasing the size and quality of habitat to landholders where Bush Stone-Curlew populations are known to exist.
Key Catchment Management Areas & Local Government Areas
Wimmera
- Hindmarsh Shire
- Horsham Rural City
- West Wimmera Shire
- Yarriambiack Shire.
Mallee
- Mildura Rural City
- Swan Hill Rural City
North Central Victoria
- Buloke Shire
- Campaspe Shire
- Gannawarra Shire
- Greater Bendigo City
- Loddon Shire
Goulburn Broken
- Benalla Rural City
- Greater Shepparton City
- Mitchell Shire
- Murrindindi Shire
- Strathbogie Shire
- Swan Hill Rural City
- Mount Alexander Shire.
North East Victoria
- Indigo Shire
- Towong Shire
- Wangaratta Rural City
- Wodonga City
Management of specific areas
Crown Land reserves: in areas that are known to be key sites for the Bush Stone-curlew there needs to be a reassessment of grazing licences to ensure Bush Stone-curlew habitat is conserved.
Puckapunyal Army Reserve and Mangalore Army Base: these sites are managed by the Department of Defence. There is an on-going commitment to fox a control program combined with monitoring the population, nesting and survival of chicks.
Parks Victoria managed reserves: where this species is known to exist in Parks there is an understanding that priority will be given to feral predator control programs at important sites within the Bush Stone-curlew's range.
Projects & Partnerships
Kowree Farm Tree Group recovery project
This project recognises the need to protect and restore the remaining population of Bush Stone-curlews in the Edenhope – Bringalbert South area. The project will:
- Promote conservation of the species.
- Be a catalyst for work to enhance the Bush Stone-curlew population.
- Develop a workable strategy for captive breeding and release.
- Engage and build local community capacity to conserve grassy woodland habitat.
- Gather information and support similar projects.
- Enhance co-operation between people in Victoria and South Australia.
- Identify and source sponsors to assist in funding the Bush Stone-curlew recovery project.

A study was carried out to determine the feasibility of developing a captive release program. The study found that due to high costs the captive release program could not proceed and has been put on hold.
Contacts:
Save our Bush Stone-curlews Project

A Population Supplementation Proposal for the Bush Stone-curlew in Central Victoria was completed by David Baker-Gabb, Elanus Pty Ltd.
This project is being run through the Mid-Loddon Sub-Catchment Management Group (Mid Loddon Landcare Network & CMN) with the Upper Spring Creek & West Marong Landcare Groups playing a vital role.
The Upper Spring Creek group is running the breeding program and West Marong Landcare Groups members provide and maintain habitats sites and Fox control, with Parks Vic supporting the forest restoration and protection. Vic Roads have provided habitat logs and litter for protected sites with recent support from the NCCMA via small Vic Landcare grants. The Sporting Shooters association also assist the group with fox control.
Five predator proof habitat sites ranging from 4 to 8 ha have been created near the Shelbourne Nature Conservation Reserve which is an 839ha public reserve 15km west of Bendigo. All sites are locked from public access and checked for feral animals. Sites are monitored by infra-red cameras to check on security and also wild Curlews.
In 2014 the group began installing Curlew breeding enclosures at Shelbourne Nature Conservation Reserve. There is also a 12 ha 'soft release enclosure' for birds to become acclimatise before being released into the local environment.
The captive breeding program has strong partnerships with the NSW Breeding & Release Program at Jindera, NSW and the NSW Curlew Program - Environment Team, Murray Local Land Services in Albury.
A Bush Stone-curlew promotional and educational display pen was established in 2013 at local Wildlife Rescue property. This will act as a focal point for community education and support for conservation activities. It will also be used as a captive breeding area for producing birds to be released into secure habitats.

Habitat restoration
In 2014, a thinning and restoration program covering 106 ha within two catchments of the Shelbourne Nature Conservation Reserve was completed. This work was done to create a wider habitat area suitable for Bush Stone-curlews as well as other threatened species in the area. This work implemented the findings from the Shelbourne Nature Conservation Reserve Soil & Vegetation Plan, 2012.
The eastern side of the reserve remains un-thinned and in a degraded condition with an increasing amount of erosion occurring on and off site.

Habitat quality
Quality habitat is critical to survival of the chicks and also adult birds. There must be an abundance of ground cover comprising leaf litter, twigs, logs etc., which can support a large population of insects, beetles lizards, frogs etc., all in close proximity to their nest.
The team have noted hatchlings often die during the first week, even in captivity but careful feeding can avoid this happening. However, in the wild if there is inadequate food and the chicks can’t find food within a few minutes they will be called back to the warmth of their mother. If this happens more than once they will probably die. This reinforces the need for quality habitat for this species to reproduce and sustain populations in the wild.
As at 2025, the project is still running but most of the birds have been moved to Mt Rothwell and for release to the Philip Island project. Only a small number of birds have been retained for a possible future reinvigoration of the breeding program which also ensures a back-up population in case of a major loss at other sites.
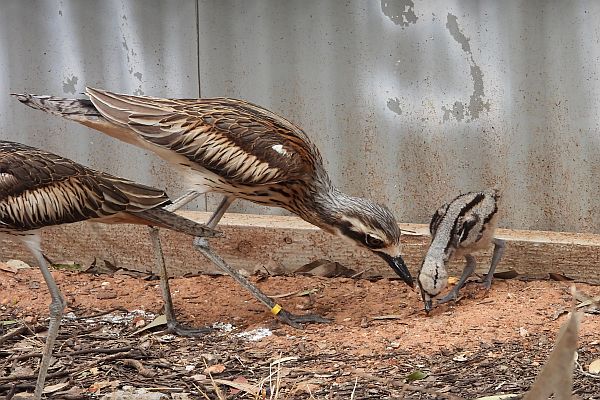

Bush Stone-curlew and chick being raised at captive breeding site as part of the Save our Bush Stone-curlew project. Image courtesy: R. Galea.
The project also included a pilot - Box Ironbark Educational Course for Primary School Students held in 2014.
The group has produced a Woodland Management Guide to assist landholders to understand and improve Woodland Ecosystems in the Mid Loddon. The guide includes a section detailing Curlew habitat requirements.
- A Glove Box Guide to Understanding and Improving Woodland Ecosystems in the Mid Loddon. (pdf) Includes a special feature on the Bush Stone-curlew as a focal species.
Mt Rothwell reintroduction project

A re-introduction of Bush Stone Curlew's to Mt Rothwell was undertaken in 2013-2014. Birds were mainly sourced from Serendip and held in a safe area for breeding then subsequently released into the area behind predator poof fencing. Contact Annette Rypalski at Mt Rothwell for further information 0434295355.

Mt Rothwell now provides a cornerstone for providing captive bred birds to other recovery projects.
Orana Sanctuary
Orana Sanctuary, approximately 1 hour north of Bendigo is a 200-hectare fenced predator free area within the much larger Orana Park estate. Bush Stone-curlews were released into the protected area in 2023 as part of a program supported by Odonata Foundation Bush stone-curlew recovery program and Tiverton Agriculture Impact Fund.
Serendip Sanctuary
Serendip Sanctuary, near Lara, is managed by Parks Victoria. Staff undertake Bush Stone-curlew captive breeding which contributes to overall conservation efforts. During 2013 and 2014 captive bred birds were provided to an interstate recovery project.
Goulburn Murray Landcare Network
A pair of curious Bush Stone-Curlews were documented as part of a project to ‘Protect icon threatened species of the Goulburn Murray Landcare area’. This project was funded by DELWP Community Volunteer Action Grant. Source: Goulburn Murray Landcare Network.
Phillip Island Nature Parks
Phillip Island Nature Parks has formed a partnership with Odonata Foundation and the Australian National University to reintroduce the Bush Stone-curlew back into the area in which it once occurred. The aim of the reintroduction program is to translocate up to 60 birds over three years from captive breeding programs which will eventually establish a self-sustaining population on Phillip Island. The initial releases are mainly sourced from captive breeding facilities at Mt Rothwell but will be supported by captive breeding operated by PINP on Phillip Island with the support of volunteers. The first release of 12 Bush Stone-curlews occurred late 2024 with an intensive monitoring program to assess their status.
View Bush Stone-curlew reintroduction – Phillip Island Nature Parks
More information:
- Phillip Island Nature Parks - Bush Stone-curlew reintroduction
- Phillip Island Nature Parks - Bush Stone-curlew reintroduction 28 November 2024 on YouTube
References & Links
- Between 2004 and 2007, (Dan Harley, Department of Environment and Heratige South Australia) and the Bush Stone-curlew regional working group undertook intensive monitoring of breeding pairs in the Bordertown and Mundulla areas to determine their nesting success. Comparisons were between Bush Stone-curlew’s on Kangaroo Island and the mainland so that some insight into fox predation can be made. Five pairs around Horsham were monitored by Jonathan Starks when he was the Bird Monitoring Co-ordinator, at the Wimmera Catchment Management Authority (no longer in this position).
- The DEPI North West is investigating habitat requirements in relation to the ratio of coarse woody debris to open ground around successful nest sites and provide recommendations on appropriate grazing regimes.
- In 2005/06 the Mallee CMA funded the Birchip Landcare group to undertake surveys in which new populations were found.
- In 2007 investigations were undertaken to assess fox predation on the survivorship and nesting success of Bush Stone-curlew populations, where exclusion fencing and/or effective fox control has been undertaken (Charles Sturt University)
- Investigate appropriate grazing strategies for different environments that conserve the Bush Stone-curlew's habitat but allow some grazing to reduce the threats of fire, weed invasion and creation of harbour for pests (Charles Sturt University).
- Encourage a post-graduate study into the species' demography to ascertain whether young birds are surviving their first year and establishing themselves in the population as breeding birds, or whether the population consists primarily of established pairs (Charles Sturt University).
- Andrew Carter, Charles Sturt University2004 - The distribution and movements of Bush Stone-curlews in
- fragmented landscapes of southern-eastern Australia.
- Elisa Tack, Charles Sturt University 2004 - Investigating management strategies to conserve the Bush Stone-curlew in agricultural land in NSW.
- Bush Stone-curlew research project, Charles Sturt University
- A Bush Stone-curlew Radio-tracking project was conducted in 2015 on a property approx. 20 km north of Corowa, NSW following the 8th release of captive-bred Bush Stone-curlews by the Nature Conservation Working Group, Contact; Elisa Tack on 0409 579 974 or elisa.tack@lls.nsw.gov.au
- VBA (2025) Victorian Biodiversity Atlas, Department of Energy, Environmnet and Climate Action (DEECA)
- VVB (2025) Visualising Victoria's Biodiversity, Federation University, Australia
More Information
- FFG Action Statement No.78 Bush Stone-curlew pdf DELWP
- FFG Threatened List (2024) Flora and Fauna Guarantee Act 1988 - Threatened List - June 2024 Department of Energy, Environment and Climate Action (DEECA), Victoria.
- Bush-stone Curlew Recovery Plan 2006 pdf - NSW Department of Environment and Conservation
- Phillip Island Nature Parks - Bush Stone-curlew reintroductionlews
- (TSCA 1995) Threatened Species Conservation Act 1995 New South Wales
- (NPWA 1972) National Parks and Wildlife Act 1972 South Australia

